
86% of students now use AI for their studies, yet only 10% of schools have established guidelines for it. This gap represents both a challenge and a massive opportunity. AI agents aren't chatbots that answer questions.
They're autonomous systems that can tutor students 24/7, predict which learners will drop out before it happens, and automate administrative queries without human intervention.
The global AI education market is projected to reach $112.3 billion by 2034, growing at 38.4% annually. Schools that implement AI agents effectively are seeing 12% higher graduation rates, 35% improved student engagement, and teachers saving 5-10 hours per week on routine tasks.
This guide breaks down exactly what AI agents do, which ones are working in real schools today, and how to implement them, whether you're a school administrator, EdTech leader, or education technology partner.
What Are AI Agents in Education?
An AI agent is an autonomous software system that can perceive its environment, make decisions, and take actions to achieve specific goals without constant human input. Unlike traditional AI tools that respond only when prompted, agents proactively monitor, adapt, and intervene.
AI Agents vs. Chatbots vs. Traditional AI
The key differentiator: AI agents don't wait for instructions. They continuously analyze student behavior, identify patterns, predict outcomes, and take action. When a student shows early signs of disengagement, the agent intervenes before a teacher even notices the problem.
Thinking About AI Agents for Your School?
We help schools figure out which AI tools actually work for their students.

Top 7 Use Cases of AI Agents in Education
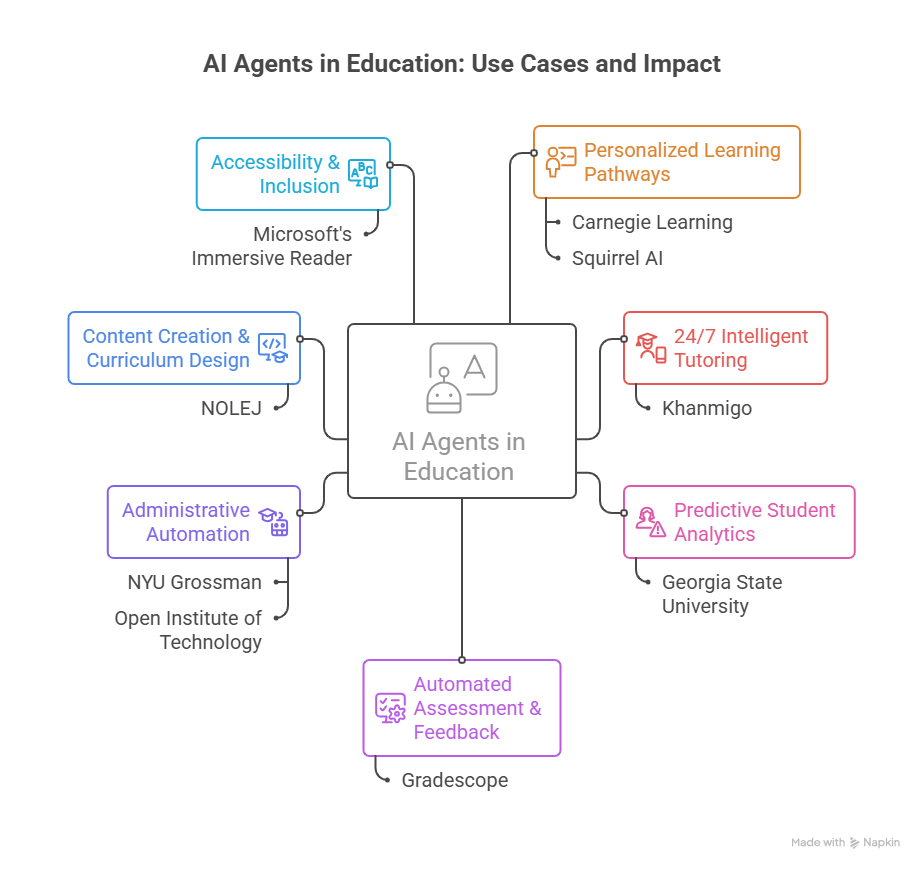
These aren't theoretical applications. Schools and universities are using AI agents today to solve real problems. Here's what's working:
1. Personalized Learning Pathways
AI agents analyze how each student learns their pace, preferred formats, knowledge gaps, and continuously adjust the curriculum. Carnegie Learning's MATHia serves 600,000+ students, identifying specific misconceptions and generating targeted exercises.
Result: 68% of students show significant learning gains versus traditional instruction. Squirrel AI in China breaks curricula into thousands of "knowledge points" and adapts lessons in real-time. Students using the platform improved scores within two months.
2. 24/7 Intelligent Tutoring
Khanmigo (Khan Academy's GPT-4 powered tutor) doesn't just give answers, it asks guiding questions, adapts explanations to each student's level, and encourages critical thinking.
In pilot programs, students reported feeling more confident in problem-solving. Teachers observed increased engagement, especially among quieter students who were hesitant to ask questions in class.
Unlike human tutors, these agents are available at 2 AM when a student is stuck on homework, and they never get frustrated repeating explanations.
3. Predictive Student Analytics
AI agents monitor attendance, assignment submissions, forum participation, and learning patterns to identify at-risk students weeks before problems become visible.
Georgia State University's GPS system generated over 250,000 advisor interventions, helping eliminate achievement gaps across demographic groups. The system identifies students who might struggle by week 3 of a course, with 74% accuracy that improves to 89% by week 15.
4. Automated Assessment & Feedback
Gradescope reduces grading time by while providing more detailed feedback than most teachers have time to write. But modern AI agents go further, they can evaluate essays for structure, argument quality, and critical thinking.
Teachers report that automated grading reduces their stress and gives them more time for high-value activities like one-on-one student interaction.
5. Administrative Automation
AI agents handle 80% of routine administrative queries, course registration, deadline reminders, and scheduling conflicts without human intervention.40% of universities now use AI for scheduling and enrollment.
NYU Grossman saved 6,000+ hours annually on application screening alone. The Open Institute of Technology (OPIT) in Europe deployed an AI agent that cut time spent on grading and correction by 30%.
6. Content Creation & Curriculum Design
AI agents generate lesson plans, quiz questions, study guides, and interactive exercises aligned with learning objectives.
NOLEJ's platform creates complete interactive learning modules within minutes. 44% of teachers now use AI for research and content gathering, 38% for lesson planning, and 37% for generating classroom materials.
7. Accessibility & Inclusion
AI agents make education accessible to students with learning disabilities. Microsoft's Immersive Reader, used in thousands of classrooms globally, helps students with dyslexia process written text.
AI translation agents subtitle lectures for non-native speakers, detect dialects, and adapt content to regional language patterns. For students with ADHD who struggle with concentration, AI tutors adjust lesson pacing and presentation format to maintain engagement.
Not Sure Where to Start with AI in Education?
Stop drowning in vendor pitches. We'll walk you through what's real, what's hype, and what fits your budget.

5 Proven Benefits of AI Agents in Education
1. Hyper-Personalization at Scale
One teacher with 30 students can't deliver individualized instruction. AI agents can. Students using AI-driven platforms score higher on average than their peers in traditional classrooms.
2. Early Intervention
AI agents can lower dropout rates by 20% by identifying struggling students before they fail. Predictive analytics catch problems that human observation misses.
3. Cost Efficiency
Schools report cost savings with AI-powered administrative systems. Johns Hopkins University reduced research costs by having AI agents handle literature reviews and documentation.
4. 24/7 Support
AI tutors don't sleep. Students can get help at midnight, on weekends, or during holidays, exactly when they often need it most.
How to Implement AI Agents in Your School
Successful AI implementation requires strategy, not just technology. Here's a proven roadmap.
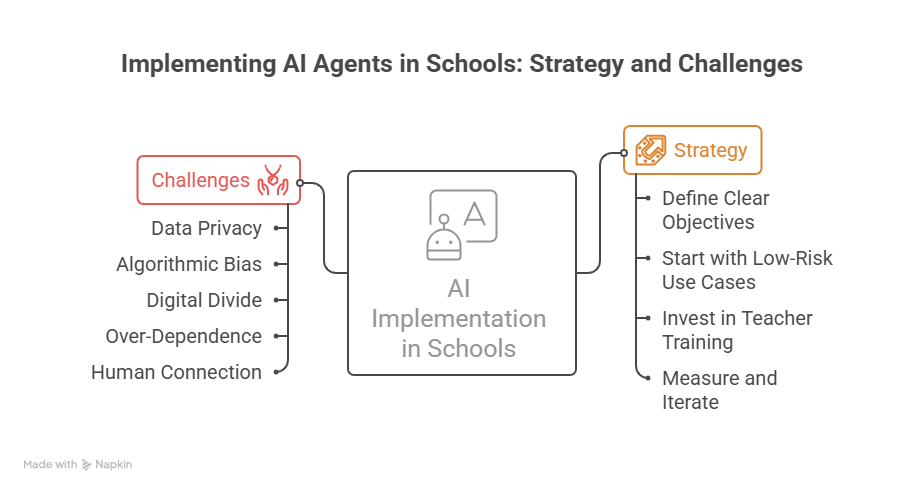
1. Define Clear Objectives
Start with specific problems: reducing dropout rates, improving math scores, automating grading, or streamlining enrollment. Vague goals like "use more AI" lead to failed pilots.
2. Start with Low-Risk Use Cases
Begin with grading assistance, accessibility support, or enrollment triage, not high-stakes assessment or student discipline. Build trust before expanding.
3. Invest in Teacher Training
Urban teachers have received no AI training. Teachers who understand AI's capabilities and limitations use it more effectively. Training should cover both technical "how-to" and pedagogical integration strategies.
4. Measure and Iterate
Track outcomes: test scores, engagement rates, time saved, student satisfaction. If something isn't working, adjust. The best implementations evolve continuously.
Challenges & Ethical Considerations
AI agents aren't a magic fix. Schools must navigate real concerns:
1. Data Privacy
Americans are more concerned than excited about AI in daily life. Student data requires strict protection, and schools have established AI usage guidelines (UNESCO).
2. Algorithmic Bias
AI trained on biased datasets can perpetuate inequities. Systems might unfairly flag students from certain demographics as "at-risk" based on historical patterns rather than individual behavior.
3. Digital Divide
Rural and underfunded schools may lack infrastructure for AI implementation. Without inclusive policies, AI benefits flow to already privileged institutions.
4. Over-Dependence
Students may become overly dependent on AI tools. Schools must teach responsible use alongside AI integration.
5. Human Connection
AI should augment teachers, not replace them. Social-emotional learning, mentorship, and peer collaboration require human relationships that technology can't replicate.
The Future: What's Coming in 2025-2026
1. Human-AI Collaborative Teaching
Expect AI agents to function as "co-teachers" handling real-time task adaptation while human educators focus on mentorship and complex discussions. Early experiments show teachers can spend less time on rote work and more on high-value interactions.
2. Emotional Intelligence in AI
Next-generation agents will detect student frustration, anxiety, or disengagement through behavioral patterns and adjust their approach. This affective computing capability will make AI tutoring feel more human and responsive.
3. Lifelong Learning Companions
AI agents will evolve into persistent learning partners that follow individuals from school through career transitions, remembering learning preferences, identifying skill gaps, and recommending development opportunities for decades.
Ready to Build Your Own AI Learning Platform?
Let's turn your vision into a system that actually helps students learn.

Conclusion
The question isn't whether AI will transform education, it's whether your institution will lead or follow. Schools that implement AI agents effectively are already seeing higher graduation rates, better student engagement, and more efficient operations.
Third Rock Techkno builds custom AI solutions for education. From intelligent tutoring systems to predictive analytics platforms, we help schools and EdTech companies implement AI that actually works. With 80+ developers specializing in AI integration and 9+ years serving EdTech clients globally, we understand both the technology and the pedagogy.
Let's Build Your AI Education Solution
Book a free consultation to discuss your requirements.
FAQs
What is an AI agent in education?
An AI agent is autonomous software that can perceive student behavior, make decisions, and take actions without constant human input. Unlike chatbots that only respond to queries, agents proactively monitor, predict, and intervene—like a 24/7 teaching assistant that never sleeps.
How much do AI agents for schools cost?
Costs vary widely. Khanmigo costs around $44/year per student. Enterprise solutions range from $10,000-$500,000+, depending on scale and customization. Many schools start with free tools (like basic ChatGPT usage) before investing in specialized platforms. The ROI typically comes from time savings, improved outcomes, and reduced dropout rates.
Can AI agents replace teachers?
No. AI agents augment teachers—they handle routine tasks so educators can focus on mentorship, critical thinking, and social-emotional support that only humans can provide. The goal is human-AI collaboration, not replacement. Schools using AI effectively report that teachers spend more time on high-value activities, not less.
What's the difference between an AI agent and a chatbot?
Chatbots respond to queries. AI agents act autonomously—they monitor student behavior, predict outcomes, and intervene proactively. A chatbot answers questions when asked. An agent notices a student is struggling and reaches out before they even ask for help.
How long does it take to implement AI in a school?
Basic tools (like grading assistants) can be deployed in days. Full-scale implementations with custom integrations typically take 3-6 months. The timeline depends on existing infrastructure, staff training needs, and the complexity of use cases. Most schools start with pilots before scaling.
.

